- Resources
Recent Activities
Plants Gallery
Downloads
Worldwide, there are plants known as psychoactive plants that naturally contain psychedelic active components. They have a high concentration of neuroprotective substances that can interact with the nervous system to produce psychedelic effects. Despite these plants' hazardous potential, recreational use of them is on the rise because of their psychoactive properties. Early neuroscience studies relied heavily on psychoactive plants and plant natural products (NPs), and both recreational and hazardous NPs have contributed significantly to the understanding of almost all neurotransmitter systems. Worldwide, there are many plants that contain psychoactive properties, and people have been using them for ages. Psychoactive plant compounds may significantly alter how people perceive the world.
Compound Summary
CAS ID |
N/A |
||
INCHI KEY |
YYGNTYWPHWGJRM-AAJYLUCBSA-N |
||
MOLECULAR WEIGHT |
410.70 |
||
MOLECULAR FORMULA |
C30H50 |
||
MOLECULAR MASS |
410.730 |
||
BIOLOGICAL SOURCE |
Lactuca virosa |
||
DATA SOURCE |
U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. 1992-2016. Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases. Home Page, http://phytochem.nal.usda.gov/ http://dx.doi.org/10.15482/USDA.ADC/1239279 | ||
CHEMICAL CLASS OF COMPOUND |
Prenol lipids |
||
NLRP3 DOCKING SCORE(Kcal/mol) |
-3.184 |
||
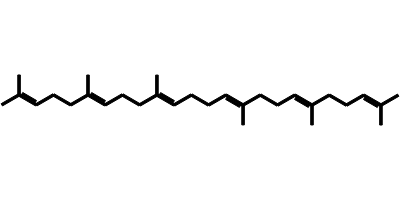
CANONICAL SMILES CC(C)=CCC/C(C)=C/CC/C(C)=C/CC/C=C(\C)CC/C=C(\C)CCC=C(C)C
|
|||
BIOACTIVITY REPORTED FOR NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASES
Yes
|
|||
SYNONYMS |
squalene, 111-02-4, Spinacene, trans-Squalene, Supraene, All-trans-Squalene, 2,6,10,15,19,23-Hexamethyltetracosa-2,6,10,14,18,22-hexaene, (E,E,E,E)-Squalene, 7683-64-9, Spinacen, (E)-Squalene, Nikko Squalane EX, (6E,10E,14E,18E)-2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyltetracosa-2,6,10,14,18,22-hexaene, Super Squalene, 2,6,10,15,19,23-Hexamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22-tetracosahexaene, 2,6,10,14,18,22-Tetracosahexaene, 2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyl-, MF59, Squalen, UNII-7QWM220FJH, 11051-27-7, EINECS 203-826-1, 7QWM220FJH, (All-E)-2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22-tetracosahexaene, (E/Z)-Squalene, CHEBI:15440, 2,6,10,14,18,22-Tetracosahexaene, 2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyl-, (all-E)-, MFCD00008912, MF59 COMPONENT SQUALENE, DTXSID0026044, HSDB 8242, EC 203-826-1, Squalene 100 microg/mL in Hexane, NCGC00181323-01, MONTANIDE ISA 720 COMPONENT SQUALENE, 2,6,10,15,19,23-Hexamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22-tetracosahexaene, (all-E)-, 2,6,10,14,18,22-Tetracosahexaene, 2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyl-, (2E,6E,10E,14E,18E)-, 2,6,10,14,18,22-tetracosahexaene, 2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyl-, (6E,10E,14E,18E)-, DTXCID406044, SQUALENE (EP MONOGRAPH), SQUALENE [EP MONOGRAPH], CAS-111-02-4, DTXSID4064767, CCRIS 711, trans-Spinacene, Super Squalene; trans-Squalene;AddaVax, NCGC00181163-01, Squalene, all-trans-, starbld0009755, SQUALENE [MI], SQUALENE [WHO-DD], SQUALENE [GREEN BOOK], Squalene, Spinacene, Supraene, CHEMBL458402, GTPL3054, QSPL 049, DTXCID8047921, HY-N1214A, HY-N1214, NSC93748, Tox21_112789, Tox21_113239, NSC-93748, s4862, AKOS015917344, CCG-268779, DB11460, 1ST40141, AS-56045, BS-49251, DA-67738, CS-0016601, CS-0201515, H0097, NS00009386, C00751, E80634, Q407560, SR-01000944749, J-002505, SR-01000944749-1, 3704365A-1DAB-4AAA-A0D0-CAE7A96723AC, 2,6,10,15,19,23-Hexamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22-tetra cosahexaene, (2E,6E,10E,14E,18E)-2,6,10,15,19,23-Hexamethyl-2,6,10,14,18,22-tetracosahexaene, 2,6,10,14,18,22-Tetracosahexene, 2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyl-,(all-E)-, 2,6,10,15,19,23-Hexamethyltetracosa-(2E,6E,10E,14E,18E,22E)-2,6,10,14,18,22-hexaene, InChI=1/C30H50/c1-25(2)15-11-19-29(7)23-13-21-27(5)17-9-10-18-28(6)22-14-24-30(8)20-12-16-26(3)4/h15-18,23-24H,9-14,19-22H2,1-8H3/b27-17+,28-18+,29-23+,30-24 |
||